【设计模式】状态模式
状态模式
- 状态模式
- 代码示例
- 查表法实现状态机
- 总结
- 状态模式与策略模式
状态模式
在 GoF 的《设计模式》⼀书中,状态模式是这么定义的:
Allow an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes.The object will appear to change its class.
状态模式又叫状态机模式,是允许对象在内部状态发生改变时改变它的行为,对象看起来好像修改了它的类。属于行为型模式。
有限状态机,英⽂翻译是 Finite State Machine,缩写为 FSM,简称为状态机。状态机有 3 个组成部分:状态(State)、事件(Event)、动作(Action)。其中,事件也称为转移条件(Transition Condition)。事件触发状态的转移及动作的执⾏。不过,动作不是必须的,也可能只转移状态,不执⾏任何动作。
状态模式的核心是状态与行为绑定,不同的状态对应不同的行为。
当对象从一种状态变为另一种状态,会触发一些行为的发生(比方说用户从订单提交到完成订单状态,可以计算对应的积分等等); 如果一个对象的状态转移过程过于复杂,可以通过将状态的判断逻辑封装到表示不同状态的一系列类中来简化其判断逻辑。
应用场景:
- 行为随状态改变而改变的场景
- 一个操作中含有庞大的多分支结构,并且这些分支取决于对象的状态。
状态模式主要包含3个角色
环境类角色(Context) : 定义客户端需要的接口,内部维护一个当前状态实例,并负责具体状态的切换。
抽象状态角色(Sate): 定义该状态下的行为,可以有一个或多个行为。
具体状态角色(ConcreteState): 具体实现该状态对应的行为,并且在需要的情况下进行状态切换。
代码示例
我们以用户下单流程的状态转换为例,用户下单会经过: 待付款, 待发货,待收货,确认收货四个状态;定义一个订单状态的枚举类,然后再定义一个状态接口,定义了所有可能的事件,如果某个状态下不支持某事件则抛出异常
//状态的枚举类
public enum OrderStatusEnum {WAIT_PAYMENT, WAIT_DELIVER, WAIT_RECEIVE, ORDER_COMPLETED;
}public interface IEvent {OrderStatusEnum getState();void pay(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception;void delive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception;void receive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception;}public class PayEvent implements IEvent {@Overridepublic OrderStatusEnum getState() {return OrderStatusEnum.WAIT_PAYMENT;}@Overridepublic void pay(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {IEvent nextEvent = new DeliveEvent();System.out.println("支付成功, 当前状态为" + nextEvent.getState());stateMachine.setEvent(nextEvent);}@Overridepublic void delive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {throw new Exception("the state" + this.getState() + "not support delive");}@Overridepublic void receive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {throw new Exception("the state" + this.getState() + "not support receive");}
}public class DeliveEvent implements IEvent {@Overridepublic OrderStatusEnum getState() {return OrderStatusEnum.WAIT_DELIVER;}@Overridepublic void pay(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {}@Overridepublic void delive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {IEvent nextEvent = new ReceiveEvent();System.out.println("已发货, 当前状态为" + nextEvent.getState());stateMachine.setEvent(nextEvent);}@Overridepublic void receive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {}}
public class ReceiveEvent implements IEvent {@Overridepublic OrderStatusEnum getState() {return OrderStatusEnum.WAIT_RECEIVE;}@Overridepublic void pay(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {throw new Exception("the state" + this.getState() + "not support pay");}@Overridepublic void delive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {throw new Exception("the state" + this.getState() + "not support delive");}@Overridepublic void receive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {IEvent nextEvent = new FinishEvent();System.out.println("确认收货, 当前状态为" + nextEvent.getState());stateMachine.setEvent(nextEvent);}
}public class FinishEvent implements IEvent{@Overridepublic OrderStatusEnum getState() {return OrderStatusEnum.ORDER_COMPLETED;}@Overridepublic void pay(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {}@Overridepublic void delive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {}@Overridepublic void receive(StateMachine stateMachine) throws Exception {}
}public class StateMachine {private IEvent event;public StateMachine() {//定义最初的事件和状态event = new PayEvent();}public void setEvent(IEvent event) {this.event = event;}public void pay() throws Exception {event.pay(this);}public void delive() throws Exception {event.delive(this);}public void receive() throws Exception {event.receive(this);}}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StateMachine stateMachine = new StateMachine();stateMachine.pay();stateMachine.delive();stateMachine.receive();System.out.println("====================");new StateMachine().delive();}}
查表法实现状态机
状态模式引入了很多状态类,在某些场景下使用查表法来实现状态机其实更加简单。
在"超级马里奥"游戏中,马里奥可以变身为多种形态。在不同的游戏情节下,各个形态会互相转化,并相应的增减积分。实际上,马里奥形态的转变就是一个状态机。比如,吃蘑菇这个事件,会触发状态的转移:从小马里奥转移到超级马里奥,以及触发动作的执行(增加 100 积分)。
对游戏背景做了简化,只保留了部分状态和事件。简化之后的状态转移如下图所示:
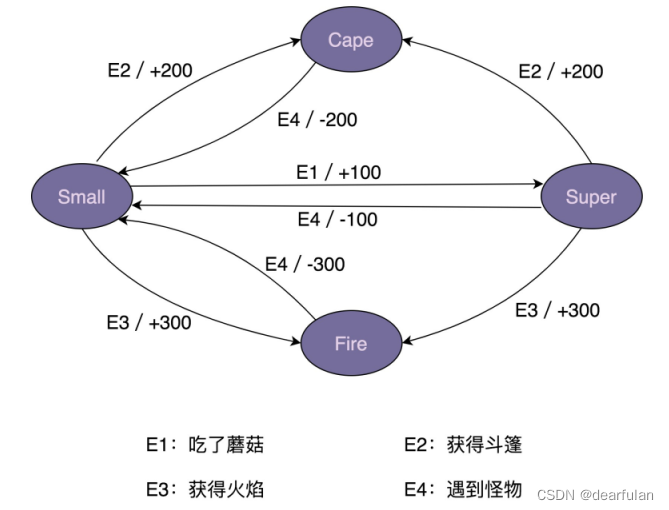
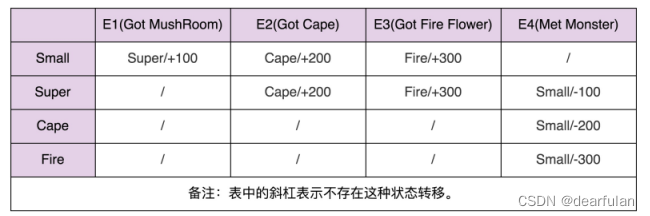
除了用状态转移图来表示之外,状态机还可以用二维表来表示,如下所示。在这个二维表中,第一维表示当前状态,第二维表示事件,值表示当前状态经过事件之后,转移到的新状态及其执行的动作。
实现代码如下:
public enum State {SMALL(0),SUPER(1),FIRE(2),CAPE(3);private int value;private State(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return this.value;}
}
public enum Event {GOT_MUSHROOM(0),GOT_CAPE(1),GOT_FIRE(2),MET_MONSTER(3);private int value;private Event(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return this.value;}
}
public class MarioStateMachine {private int score;private State currentState;private static final State[][] transitionTable = {{SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL},{SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL},{CAPE, CAPE, CAPE, SMALL},{FIRE, FIRE, FIRE, SMALL}};private static final int[][] actionTable = {{+100, +200, +300, +0},{+0, +200, +300, -100},{+0, +0, +0, -200},{+0, +0, +0, -300}};public MarioStateMachine() {this.score = 0;this.currentState = State.SMALL;}public void obtainMushRoom() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_MUSHROOM);}public void obtainCape() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_CAPE);}public void obtainFireFlower() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_FIRE);}public void meetMonster() {executeEvent(Event.MET_MONSTER);}private void executeEvent(Event event) {int stateValue = currentState.getValue();int eventValue = event.getValue();this.currentState = transitionTable[stateValue][eventValue];this.score = actionTable[stateValue][eventValue];}public int getScore() {return this.score;}public State getCurrentState() {return this.currentState;}}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MarioStateMachine mario = new MarioStateMachine();mario.obtainMushRoom();int score = mario.getScore();State state = mario.getCurrentState();System.out.println("mario score: " + score + "; state: " + state);}
}游戏这种⽐较复杂的状态机,包含的状态⽐较多,优先推荐使⽤查表法,因为状态模式会引⼊⾮常多的状态类,导致代码⽐较难维护。而类似用户下单这种操作的状态机,它们的状态并不多,状态转移也⽐较简单,但触发的业务逻辑比较复杂,更适合使用状态模式
总结
优点
- 结构清晰,状态模式将与特定状态相关的行为封装到一个状态类中,并将不同状态的行为分割开来,满足“单一职责原则”,
- 状态类职责明确,有利于扩展新的状态和转换关系
缺点
- 状态模式的使用必然会增加系统的类与对象的个数。
- 状态模式对开闭原则的支持并不太好,对于可以切换状态的状态模式,增加新的状态类需要修改那些负责状态转换的源码,否则无法切换到新增状态,而且修改某个状态类的行为也需要修改对应类的代码。
状态模式与策略模式
状态模式和策略模式的UML类图很像(策略模式也包含三种角色:Context ,Strategy,ConcreteStrategy),但其使用场景是完全不一样的。
策略模式的多种算法任选其一都可以满足你的要求,算法之间彼此独立,但是状态模式各个状态之间是存在关联关系的,在一定条件下还可以相互转换,用户无法指定状态,只能设置初始状态。
上述"超级马里奥"的例子选自极客时间<<设计模式之美>> 专栏
上一篇:谈谈嵌入式软件兼容性
