IO学习、拓展贴
创始人
2024-05-30 18:38:26
1. 字节流
1.1 FileInputStream
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;/*** 演示FileInputStream的使用(字节输入流 文件--> 程序)*/
public class FileInputStream_ {public static void main(String[] args) {}/*** 演示读取文件...* 单个字节的读取,效率比较低* -> 使用 read(byte[] b)*/@Testpublic void readFile01() {String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";int readData = 0;FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;try {//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char)readData);//转成char显示}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//关闭文件流,释放资源.try {fileInputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 使用 read(byte[] b) 读取文件,提高效率*/@Testpublic void readFile02() {String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";//字节数组byte[] buf = new byte[8]; //一次读取8个字节.int readLen = 0;FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;try {//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);//从该输入流读取最多b.length字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕//如果读取正常, 返回实际读取的字节数while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));//显示}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//关闭文件流,释放资源.try {fileInputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
read()方法:返回-1表示读取完毕
read(byte[] buf):返回实际读取的长度
使用 read(byte[] b) 读取文件,提高效率
1.2 FileOutputStream
1.2.1 在文件中写入内容
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;public class FileOutputStream01 {public static void main(String[] args) {}/*** 演示使用FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中,* 如果该文件不存在,则创建该文件*/@Testpublic void writeFile() {//创建 FileOutputStream对象String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;try {//得到 FileOutputStream对象 对象//老师说明//1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容//2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true);//写入一个字节//fileOutputStream.write('H');////写入字符串String str = "hsp,world!";//str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组//fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());/*write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流*/fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, 3);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {fileOutputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
1.FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
参数true表示追加
2.write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
3.write(‘H’)
输出到文件中的是字符
4.write(97)
输出到文件中的是字符
1.2.2 图片、音乐、视频的复制
import com.hspedu.inputstream_.FileInputStream_;import java.io.*;/*** @version 1.0*/
public class FileCopy {public static void main(String[] args) {//完成 文件拷贝,将 e:\\Koala.jpg 拷贝 c:\\//思路分析//1. 创建文件的输入流 , 将文件读入到程序//2. 创建文件的输出流, 将读取到的文件数据,写入到指定的文件.String srcFilePath = "e:\\Koala.jpg";String destFilePath = "e:\\Koala3.jpg";FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;try {fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);//定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果byte[] buf = new byte[1024];int readLen = 0;while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {//读取到后,就写入到文件 通过 fileOutputStream//即,是一边读,一边写fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen);//一定要使用这个方法}System.out.println("拷贝ok~");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {//关闭输入流和输出流,释放资源if (fileInputStream != null) {fileInputStream.close();}if (fileOutputStream != null) {fileOutputStream.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}2. 字符流
2.1 FileReader
package com.hspedu.reader_;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class FileReader_ {public static void main(String[] args) {}/*** 单个字符读取文件*/@Testpublic void readFile01() {String filePath = "e:\\story.txt";FileReader fileReader = null;int data = 0;//1. 创建FileReader对象try {fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);//循环读取 使用read, 单个字符读取while ((data = fileReader.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) data);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (fileReader != null) {fileReader.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 字符数组读取文件*/@Testpublic void readFile02() {System.out.println("~~~readFile02 ~~~");String filePath = "e:\\story.txt";FileReader fileReader = null;int readLen = 0;char[] buf = new char[8];//1. 创建FileReader对象try {fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);//循环读取 使用read(buf), 返回的是实际读取到的字符数//如果返回-1, 说明到文件结束while ((readLen = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (fileReader != null) {fileReader.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}2.2 FileWriter
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class FileWriter_ {public static void main(String[] args) {String filePath = "e:\\note.txt";//创建FileWriter对象FileWriter fileWriter = null;char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c'};try {fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);//默认是覆盖写入
// 3) write(int):写入单个字符fileWriter.write('H');
// 4) write(char[]):写入指定数组fileWriter.write(chars);
// 5) write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分fileWriter.write("韩顺平教育".toCharArray(), 0, 3);
// 6) write(string):写入整个字符串fileWriter.write(" 你好北京~");fileWriter.write("风雨之后,定见彩虹");
// 7) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分fileWriter.write("上海天津", 0, 2);//在数据量大的情况下,可以使用循环操作.} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//对应FileWriter , 一定要关闭流,或者flush才能真正的把数据写入到文件//看源码就知道原因./*看看代码private void writeBytes() throws IOException {this.bb.flip();int var1 = this.bb.limit();int var2 = this.bb.position();assert var2 <= var1;int var3 = var2 <= var1 ? var1 - var2 : 0;if (var3 > 0) {if (this.ch != null) {assert this.ch.write(this.bb) == var3 : var3;} else {this.out.write(this.bb.array(), this.bb.arrayOffset() + var2, var3);}}this.bb.clear();}*/try {//fileWriter.flush();//关闭文件流,等价 flush() + 关闭fileWriter.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("程序结束...");}
}1.可以以字符、数字、字符数组、字符串方式写出
2.可以指定字符数组字符串的区间输出
3.必须执行flush方法才能够将数据写入文件,否则没有效果
4.字符流的close方法嵌套了flush
3. 流的分类
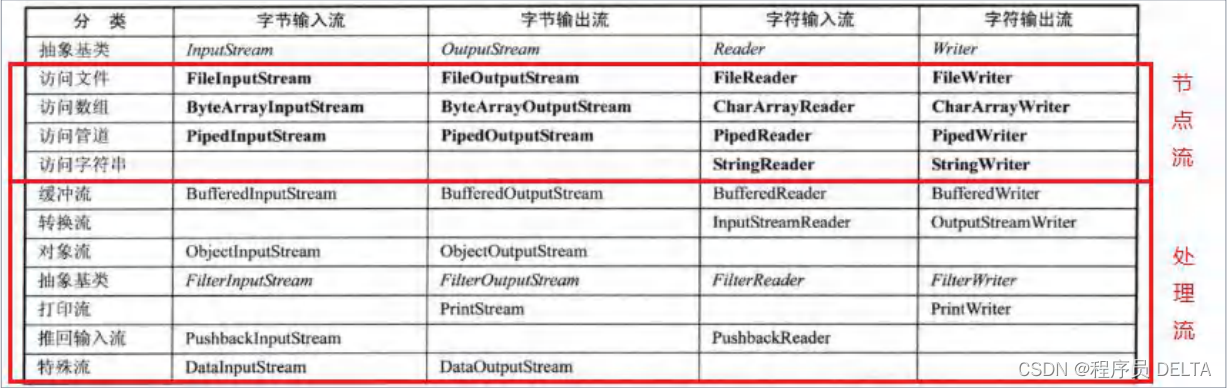
记住节点流和处理流(包装流)这些名词
3.1 节点流和处理流的区别

3.2 处理流的主要功能和好处

4. 缓冲流
4.1 bufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;/*** 演示bufferedReader 使用*/
public class BufferedReader_ {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String filePath = "e:\\a.java";//创建bufferedReaderBufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));//读取String line; //按行读取, 效率高//说明//1. bufferedReader.readLine() 是按行读取文件//2. 当返回null 时,表示文件读取完毕while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}//关闭流, 这里注意,只需要关闭 BufferedReader ,因为底层会自动的去关闭 节点流//FileReader。/*public void close() throws IOException {synchronized (lock) {if (in == null)return;try {in.close();//in 就是我们传入的 new FileReader(filePath), 关闭了.} finally {in = null;cb = null;}}}*/bufferedReader.close();}
}
1.关闭处理流时,只需要关最外层的即可,底层做了封装
2.缓冲流性能效率更好,提供了例如readLine()等方法
下一篇:[数据库]内置函数
相关内容
热门资讯
最新或2023(历届)石家庄市...
最新或2023(历届)石家庄五险一金 1、缴存基数计算口径及标准。住房公积金缴存基数为职工上一年...
最新或2023(历届)河北省五...
最新或2023(历届)河北工资扣税标准也是3500元。 一、最新或2023(历届)河北工资扣税规定...
最新或2023(历届)国家网络...
今年4月19日习近平总书记在网络安全和信息化工作座谈会上发表重要讲话,明确提出“网络安全为人民,网络...
最新或2023(历届)青海省上...
最新或2023(历届)上班期间哺乳假规定,哺乳假工资待遇怎么算 最新或2023(历届)上班期间哺乳...
最新或2023(历届)毕节市上...
最新或2023(历届)上班期间哺乳假规定,哺乳假工资待遇怎么算 最新或2023(历届)上班期间哺乳...
