Java基础之异常处理
创始人
2024-05-20 10:45:29
一、小试牛刀
num1 / num2
当除数为零时,程序就会抛出异常,程序就会崩溃而导致退出。
我们可以通过异常处理机制来解决该问题
如果我们认为一段代码可能发生异常,可以使用try-catch-finally异常处理机制来解决。从而保证程序的健壮性。
将可能发生异常的代码选中,按快捷键(Ctrl + Alt + t)选中(try-catch-finally)
如果异常发生了,则异常后面的代码不会执行,将会直接跳到catch语句当中,执行catch中的代码。
如果异常没有发生,则会顺序执行try语句中的代码,不会跳到catch语句当中。
public class DemoException {public static void main(String[] args){Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int num1 = scanner.nextInt();int num2 = scanner.nextInt();try {int res = num1 / num2;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 输出异常信息// e.printStackTrace();System.out.println(e);}// finally语句一般都是用于处理关闭连接或者释放资源finally{scanner.close();System.out.println("无论是否发生异常,该语句都会执行下去...");}System.out.println("程序继续...");}
}
5
0
/ by zero
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
无论是否发生异常,该语句都会执行下去...
程序继续...
二、异常体系图
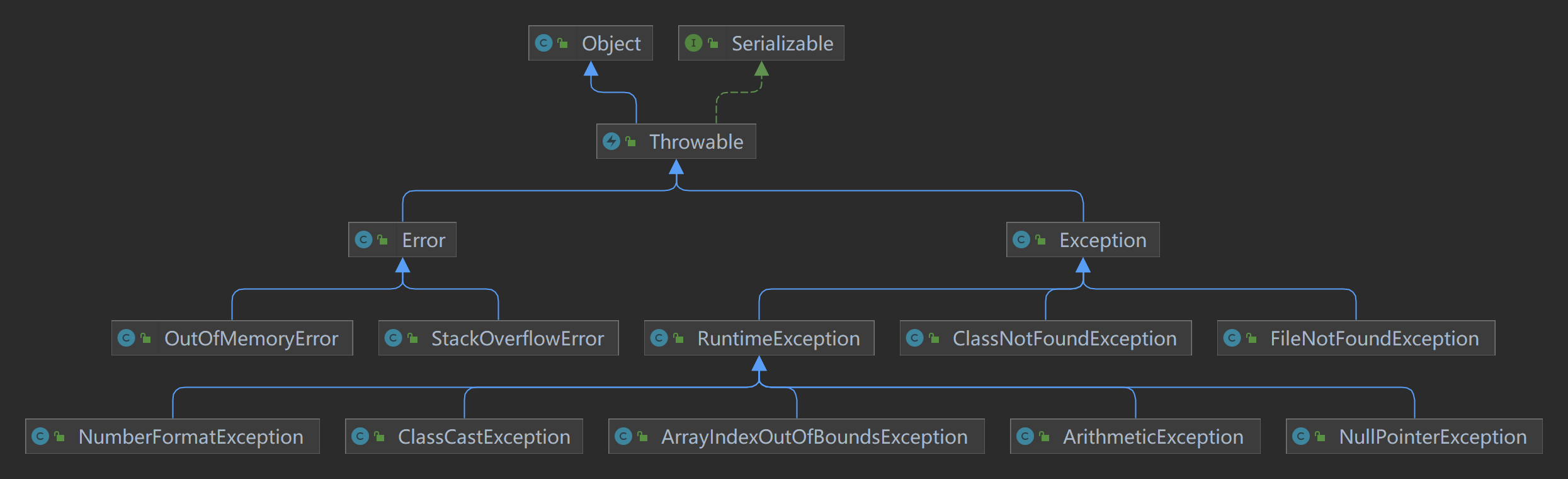
三、常见的运行时异常
3.1 NullPointerException(空指针异常)
package cn.github.wangpeng.exception;import cn.github.wangpeng.Student;public class NullPointerEx {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = null;System.out.println(stu.getAge());} }
3.2 ClassCastException(类型转换异常)
package cn.github.wangpeng.exception;
public class ClassCastEx {public static void main(String[] args) {Animal animal = new Cat();Dog dog = (Dog)animal;}
}
class Animal{}
class Cat extends Animal{}
class Dog extends Animal{}
3.3 NumberFormatException(数字格式异常)
package cn.github.wangpeng.exception;public class NumberFormatEx {public static void main(String[] args) {String num = "abc";System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(num));}
}
四、常见的编译时异常
编译异常是指在编译期间,就必须处理的异常,否则代码不能通过编译。
public class DemoInputStream {public static void main(String[] args) {String filePath = "Basic\\demo2.txt";int readData = 0;FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;try {// 创建FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件。fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);// public int read() throws IOException 从此输入流中读取一个字节的数据。while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char)readData);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {// 关闭文件流 释放资源fileInputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
五、异常处理方式
异常处理方式有两种:
1.自行捕获异常 (try-catch-finally)
2.将发生的异常抛出,交给调用者(方法)来处理,最顶级的处理者时JVM (throws)
注意:
在方法声明中用throws语句声明异常,throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类
对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,try-catch-finally 或者 throws都可以
对于运行异常,如果程序中没有处理,则默认使用throws的处理方式

public static void f1() {// 编译异常有两种解决办法// 1.使用异常捕获try-catch-finally// 2.使用抛出异常throws,让调用f1方法的调用者(方法)来处理try {FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream("");} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
public static void f2() throws FileNotFoundException {FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("");}
public static void f3() {// 对于运行时异常,程序中没有处理,默认就是throws的方法来处理int n1 = 10;int n2 = 0;int res = n1 / n2;}
class Father {public void method() throws RuntimeException {}
}class Son extends Father {// 子类重写父类方法的时候,注意:子类重写的方法所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,// 要么为父类抛出异常类型的子类型@Overridepublic void method() throws NullPointerException {}
}
六、自定义异常
public class DemoExceptionCustomise {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("请输入您的年龄:");Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int age = scanner.nextInt();if (!(age > 0 && age < 100)) {// 这里通过构造器来设置信息,throw后面是具体的异常对象throw new AgeException("年龄不合法!!!");}}
}class AgeException extends RuntimeException {public AgeException(String message) {super(message);}
}

相关内容
热门资讯
最新或2023(历届)关于铁人...
王进喜,1923年10月8日出生于甘肃省玉门县赤金堡一个贫苦的农民家庭。6岁讨饭,10岁给地主放牛,...
最新或2023(历届)森林防火...
森林防火须知手抄报图片
原创 半...
朝方突然甩出一份声明,把刚有点缓和苗头的半岛,一脚踹回了紧张模式。 2025新年钟声才敲响几天,...
