Lua C接口编程(二)
创始人
2024-05-11 07:23:15
引言
上篇文章我们学习了C如何调用Lua,今天我们就来聊聊Lua 如何调用C。
Lua版本:Lua 5.3.5
对于Lua提供的接口有不清楚的,可以参考Lua接口官方文档
一、Lua调用C步骤
- 需要将C文件编译成动态库
- 在Lua文件中使用package.cpath配置C动态库路径
- 使用require 关键字引入指定C文件
因为Lua只认识.so文件,会去识别以 luaopen_* 开头的函数执行。
二、代码示例
2.1 lua 通过调用C中的方法将自己参数打印到终端
Lua源文件 test-tbl.lua
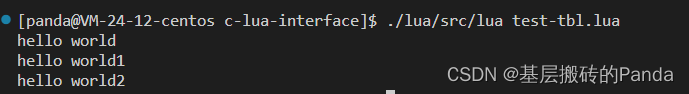
package.cpath = "./?.so" --c库的路径local so = require "tbl.c" -- 这里xxx.c 对应 xxx.so 动态库so.echo("hello world") -- 新的虚拟栈
so.echo("hello world1")-- 新的虚拟栈
so.echo("hello world2")-- 新的虚拟栈
C源文件 lua-tbl.c
#include
#include
#include
#include static int
lecho (lua_State *L) {const char* str = lua_tostring(L, -1);fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", str);return 0;
}static const luaL_Reg l[] = {// 导出给lua使用数组{"echo", lecho},{NULL, NULL},
};int
luaopen_tbl_c(lua_State *L) { // local tbl = require "tbl.c"// 创建一张新的表,并预分配足够保存下数组 l 内容的空间luaL_newlib(L, l);return 1;
}
编译 lua-tbl.c 文件为动态库:
gcc lua-tbl.c -fPIC -shared -o tbl.so -Wall
就会在当前目录会生成 tbl.so 文件,执行 lua test-tbl.lua
运行结果:
2.2 userdata 实战应用
Lua源文件 test-ud.lua
package.cpath = "./?.so"
local so = require "ud.c"local ud = so.new()ud:echo("hello world1")
ud:again()
ud:echo("hello world2")
ud:again()
ud:echo("hello world3")
ud:again()
--./lua/src/lua test-ud.lua
C源文件 lua-ud.c
#include
#include
#include #include
#include
#include struct log {int count;
};static int
lagain(lua_State *L) {struct log *p = (struct log *)luaL_checkudata(L, 1, "mk.ud.log");lua_getuservalue(L, -1);const char* str = lua_tostring(L, -1);fprintf(stdout, "ud[n=%d]----%s\n", p->count, str);return 0;
}static int
lecho(lua_State *L) {/*void *luaL_checkudata (lua_State *L, int arg, const char *tname);检查arg是不是userdata类型,如果是 返回userdata的内存地址*/struct log *p = (struct log *)luaL_checkudata(L, 1, "mk.ud.log");const char* str = lua_tostring(L, -1);p->count++;// Pops a value from the stack and sets it as the new n-th user value associated to the full userdata at the given index. Returns 0 if the userdata does not have that value.lua_setuservalue(L, -2);fprintf(stdout, "ud[n=%d]----%s\n", p->count, str);return 0;
}static int
lnew (lua_State *L) {struct log *q = (struct log*)lua_newuserdata(L, sizeof(struct log));q->count = 0;lua_pushstring(L, "");lua_setuservalue(L, -2);// 如果key(mk.ud.log) 存在,返回0; 否则为userdata创建一个新表table,插入__name = mk.ud.log, 为注册表添加 [mk.ud.log] = table 返回1if (luaL_newmetatable(L, "mk.ud.log")) {luaL_Reg m[] = {{"echo", lecho},{"again", lagain},{NULL, NULL},};luaL_newlib(L, m);lua_setfield(L, -2, "__index"); // LUA_REGISTRYINDEX[__index] = stackTopElem// int lua_setmetatable (lua_State *L, int index);// Pops a table or nil from the stack and sets that value as the new metatable for the value at the given index.// 从栈顶弹出一个table或者nil, 将该值设置为给定索引index的新元表lua_setmetatable(L, -2);}return 1;
}static const luaL_Reg l[] = {{"new", lnew},{NULL, NULL},
};int
luaopen_ud_c(lua_State *L) {luaL_newlib(L, l);return 1;
} 编译 lua-ud.c 文件为动态库:
gcc lua-ud.c -fPIC -shared -o ud.so -Wall
就会在当前目录会生成 ud.so 文件,执行 lua test-ud.lua
运行结果:

2.3 upvalue上值实战应用
Lua源文件 test-uv.lua
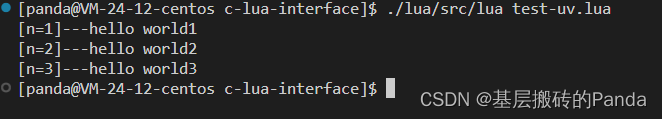
package.cpath = "./?.so"local so = require "uv.c"so.echo("hello world1")
so.echo("hello world2")
so.echo("hello world3")
C源文件 lua-uv.c
#include #include #include #include // 闭包实现: 函数 + 上值 luaL_setfuncs
/*int lua_upvalueindex (int i);函数返回一个伪索引,这个伪索引是 i位置表示的上值 i 的范围 [1, 256]Returns the pseudo-index that represents the i-th upvalue of the running function (see §4.2). i must be in the range [1,256].
*/
// lua_upvalueindex(1)
// lua_upvalueindex(2)static int
lecho (lua_State *L) {lua_Integer n = lua_tointeger(L, lua_upvalueindex(1));n++;const char* str = lua_tostring(L, -1);fprintf(stdout, "[n=%lld]---%s\n", n, str);lua_pushinteger(L, n);lua_replace(L, lua_upvalueindex(1));return 0;
}static const luaL_Reg l[] = {{"echo", lecho},{NULL, NULL}, // 必须以{NULL, NULL},结尾
};int
luaopen_uv_c(lua_State *L) { // local tbl = require "tbl.c"luaL_newlibtable(L, l);// 1lua_pushinteger(L, 0);// 2/*void luaL_setfuncs (lua_State *L, const luaL_Reg *l, int nup);将l数组中所有的function 注册到栈顶的table中当 nup 不为零时,所有函数都使用 nup up值创建,并使用先前推送到库表顶部堆栈上的 nup 值的副本进行初始化*/luaL_setfuncs(L, l, 1);// 上值// luaL_newlib(L, l);return 1;
} 编译 lua-uv.c 文件为动态库:
gcc lua-uv.c -fPIC -shared -o uv.so -Wall
就会在当前目录会生成 uv.so 文件,执行 lua test-uv.lua
运行结果:
上一篇:二叉树的基本操作
相关内容
热门资讯
最新或2023(历届)保定市...
节,指的是农历正月初一,又叫阴历年,俗称“过年”。这是我国民间最隆重、最热闹的一个传统节日。春节由虞...
最新或2023(历届)秦皇岛...
春节期间,北戴河区主打“文化牌”,在集发观光园推出“春节大游园”和“冬韵摄影展”活动,突出趣味性、观...
机电技术教育专业大学生职业规划...
初入大学就应该树立正确的职业生涯规划理念,大一就进行职业规划,从一开始就不走弯路。 大一、大二 ...
大一新生纺织工艺教育专业个人职...
初入大学就应该树立正确的职业生涯规划理念,大一就进行职业规划,从一开始就不走弯路。 大学一年级 ...
大学新生服装设计与工艺教育专业...
摘要:服装设计与工艺教育专业毕业生的基本素质 1、掌握服装设计与工艺专业的基本理论、基本知识和基...
