JUC-线程安全集合类
章节目录:
- 一、概述
- 二、ConcurrentHashMap
- 2.1 并发问题
- 2.2 重要属性和内部类
- 2.3 重要方法
- 2.4 构造器
- 2.5 get 流程
- 2.6 put 流程
- 2.7 size 计算流程
- 2.8 对比 JDK 7 的 ConcurrentHashMap 有什么区别?
- 三、LinkedBlockingQueue
- 3.1 入队出队
- 3.2 加锁分析
- 3.3 线程安全分析
- 3.4 源码分析
- 3.5 性能比较
- 四、ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- 4.1 概述
- 4.2 简单实现
- 五、CopyOnWriteArrayList
- 5.1 源码分析
- 5.2 弱一致性
- 六、结束语
一、概述
在
Java中线程安全集合类可以分为三大类。
- 遗留的线程安全集合:
Hashtable、Vector; Collections装饰的线程安全集合:

java.util.concurrent.*下的线程安全集合类,其中包含的又有以下三类关键词:
-
Blocking:大部分实现基于锁,并提供用来阻塞的方法。
-
CopyOnWrite:之类容器修改开销相对较重。
-
Concurrent:类型的容器,内部很多操作使用
cas优化,一般可以提供较高吞吐量,另外它还有弱一致性的特点:- 遍历时弱一致性,例如,当利用迭代器遍历时,如果容器发生修改,迭代器仍然可以继续进行遍历,这时内容是旧的;
- 求大小弱一致性,size 操作未必是 100% 准确;
- 读取弱一致性。
二、ConcurrentHashMap
2.1 并发问题
- 代码示例:
public class Demo {private static final String ALPHA = "abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";private static final List TEST_DATA = new ArrayList<>();static {int length = ALPHA.length();int count = 100;int capacity = length * count;List list = new ArrayList<>(capacity);for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {// 拿到每个字母。char c = ALPHA.charAt(i);for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {// 添加字母各一百次到集合中。list.add(c + "");}}// 将集合中元素随机重排序。Collections.shuffle(list);TEST_DATA.addAll(list);}/*** 获取计数结果。** @param threadNum 线程数。* @param sup 供给型函数式接口。* @param cons 消费型函数式接口。*/private static void getCount(int threadNum,Supplier> sup,BiConsumer, List> cons) {Map map = sup.get();List threads = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {Thread t = new Thread(() -> cons.accept(map, TEST_DATA));threads.add(t);}threads.forEach(Thread::start);threads.forEach(t -> {try {t.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}});System.out.println(map);}/*** 方式一:使用非线程安全的 `map` 并发读取。*/@Testpublic void test02() {getCount(2,() -> new HashMap(),(map, words) -> {for (String word : words) {Integer counter = map.get(word);int newValue = counter == null ? 1 : counter + 1;map.put(word, newValue);}});// {a=193, b=192, c=196, d=197, e=193, f=193, g=195, h=195, i=193,// j=192, k=196, l=193, m=191, n=192, o=198, p=192, q=197, r=193,// s=192, t=175, u=194, v=193, w=193, x=195, y=191, z=195}}/*** 方式二:使用 `ConcurrentHashMap` 并发读取。*/@Testpublic void test03() {getCount(2,() -> new ConcurrentHashMap(),(map, words) -> {for (String word : words) {// 函数式编程,无需原子变量。map.merge(word, 1, Integer::sum);}});// {a=200, b=200, c=200, d=200, e=200, f=200, g=200, h=200, i=200,// j=200, k=200, l=200, m=200, n=200, o=200, p=200, q=200, r=200,// s=200, t=200, u=200, v=200, w=200, x=200, y=200, z=200}}
}
2.2 重要属性和内部类
备注:此处示例为
JDK 8版本,数组简称(table),链表简称(bin)。
// 默认为 0
// 当初始化时, 为 -1
// 当扩容时, 为 -(1 + 扩容线程数)
// 当初始化或扩容完成后,为 下一次的扩容的阈值大小
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;// 整个 ConcurrentHashMap 就是一个 Node[]
static class Node implements Map.Entry {}// hash 表
transient volatile Node[] table;// 扩容时的 新 hash 表
private transient volatile Node[] nextTable;// 扩容时如果某个 bin 迁移完毕, 用 ForwardingNode 作为旧 table bin 的头结点
static final class ForwardingNode extends Node {}// 用在 compute 以及 computeIfAbsent 时, 用来占位, 计算完成后替换为普通 Node
static final class ReservationNode extends Node {}// 作为 treebin 的头节点, 存储 root 和 first
static final class TreeBin extends Node {}// 作为 treebin 的节点, 存储 parent, left, right
static final class TreeNode extends Node {}
2.3 重要方法
// 获取 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node
static final Node tabAt(Node[] tab, int i)// cas 修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, c 为旧值, v 为新值
static final boolean casTabAt(Node[] tab, int i, Node c, Node v)// 直接修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, v 为新值
static final void setTabAt(Node[] tab, int i, Node v)
2.4 构造器
实现了懒惰初始化,在构造方法中仅仅计算了
table大小,之后会在第一次使用时才会真正的创建。
/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,* given the specified load factor.* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for* establishing the initial table size* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as* a sizing hint.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are* nonpositive*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many binsinitialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads// tableSizeFor 保证计算大小是(2^n):即16、32、64...long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);this.sizeCtl = cap;}
2.5 get 流程
/*** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.** More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)** @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null*/public V get(Object key) {Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;// spread 方法能确保返回结果是正数。int h = spread(key.hashCode());if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {// 如果头节点已经是要查找的 key。if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))return e.val;}// hash 为负数表示该 bin 在扩容中或是 treebin, 这时调用 find 方法来查找。else if (eh < 0)return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;// 正常遍历链表, 用 equals 比较。while ((e = e.next) != null) {if (e.hash == h &&((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))return e.val;}}return null;}
2.6 put 流程
put():
/*** Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table.* Neither the key nor the value can be null.** The value can be retrieved by calling the {@code get} method* with a key that is equal to the original key.** @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null*/public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(key, value, false); // *** putVal() 具体方法说明在下方 ***}
putVal():
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();// 其中 spread 方法会综合高位低位, 具有更好的 hash 性。int hash = spread(key.hashCode());int binCount = 0;for (Node[] tab = table;;) {// f 是链表头节点;// fh 是链表头结点的 hash;// i 是链表在 table 中的下标。Node f; int n, i, fh;// 要创建 table。if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)// 初始化 table 使用了 cas, 无需 synchronized 创建成功, 进入下一轮循环。 tab = initTable(); // *** initTable() 具体方法说明在下方 ***// 要创建链表头节点。else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {// 添加链表头使用了 cas, 无需 synchronized。if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node(hash, key, value, null)))break; // no lock when adding to empty bin}// 帮忙扩容。else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);else {V oldVal = null;// 锁住链表头节点。synchronized (f) {// 再次确认链表头节点没有被移动。if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {if (fh >= 0) {binCount = 1;// 遍历链表。for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {K ek;// 找到相同的key。if (e.hash == hash &&((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {oldVal = e.val;// 值更新。if (!onlyIfAbsent)e.val = value;break;}Node pred = e;// 已经是最后的节点了, 新增 Node, 追加至链表尾。if ((e = e.next) == null) {pred.next = new Node(hash, key,value, null);break;}}}// 红黑树。else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {Node p;binCount = 2;// putTreeVal 会看 key 是否已经在树中, 是, 则返回对应的 TreeNode。if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,value)) != null) {oldVal = p.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)p.val = value;}}}// 释放链表头节点的锁。}if (binCount != 0) {if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)// 如果链表长度 >= 树化阈值(8), 进行链表转为红黑树。treeifyBin(tab, i);if (oldVal != null)return oldVal;break;}}}// 增加 size 计数。addCount(1L, binCount); // *** addCount() 具体方法说明在下方 ***return null;}
initTable():
/*** Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.*/private final Node[] initTable() {Node[] tab; int sc;while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin// 尝试将 sizeCtl 设置为 -1(表示初始化 table)。else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {// 获得锁, 创建 table, 这时其它线程会在 while() 循环中 yield 直至 table 创建。try {if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Node[] nt = (Node[])new Node[n];table = tab = nt;sc = n - (n >>> 2);}} finally {sizeCtl = sc;}break;}}return tab;}
addCount():
/*** Adds to count, and if table is too small and not already* resizing, initiates transfer. If already resizing, helps* perform transfer if work is available. Rechecks occupancy* after a transfer to see if another resize is already needed* because resizings are lagging additions.** @param x the count to add* @param check if <0, don't check resize, if <= 1 only check if uncontended*/// check 是之前 binCount 的个数。private final void addCount(long x, int check) {CounterCell[] as; long b, s;// 已经有了 counterCells, 向 cell 累加。if ((as = counterCells) != null ||// 还没有, 向 baseCount 累加。!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {CounterCell a; long v; int m;boolean uncontended = true;// 还没有 counterCells。if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||// 还没有 cell。(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||// cell cas 增加计数失败。!(uncontended =U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {// 创建累加单元数组和cell, 累加重试。fullAddCount(x, uncontended);return;}if (check <= 1)return;// 获取元素个数。s = sumCount();}if (check >= 0) {Node[] tab, nt; int n, sc;while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {int rs = resizeStamp(n);if (sc < 0) {if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||transferIndex <= 0)break;// newtable 已经创建了,帮忙扩容。if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))transfer(tab, nt);}// 需要扩容,这时 newtable 未创建。else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))transfer(tab, null);s = sumCount();}}}
2.7 size 计算流程
size计算实际发生在put,remove改变集合元素的操作之中。- 没有竞争发生,向 baseCount 累加计数。
- 有竞争发生,新建 counterCells,向其中的一个 cell 累加计数:
- counterCells 初始有两个 cell。
- 如果计数竞争比较激烈,会创建新的 cell 来累加计数。
/*** {@inheritDoc}*/public int size() {long n = sumCount();return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :(int)n);}final long sumCount() {CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;// 将 baseCount 计数与所有 cell 计数累加。long sum = baseCount;if (as != null) {for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {if ((a = as[i]) != null)sum += a.value;}}return sum;}
Java 8 数组(Node) +( 链表 Node | 红黑树 TreeNode ) 以下数组简称(table),链表简称(bin):
- 初始化:使用
cas来保证并发安全,懒惰初始化table; - 树化:当 table.length < 64 时,先尝试扩容,超过 64 时,并且 bin.length > 8 时,会将链表树化,树化过程会用
synchronized锁住链表头; - put:如果该
bin尚未创建,只需要使用cas创建bin;如果已经有了,锁住链表头进行后续put操作,元素添加至bin的尾部; - get:无锁操作仅需要保证可见性,扩容过程中 get 操作拿到的是 ForwardingNode 它会让
get操作在新table进行搜索; - 扩容:扩容时以
bin为单位进行,需要对bin进行synchronized,但这时妙的是其它竞争线程也不是无事可做,它们会帮助把其它bin进行扩容,扩容时平均只有 1/6 的节点会把复制到新table中; - size:元素个数保存在 baseCount 中,并发时的个数变动保存在 CounterCell[] 当中。最后统计数量时累加即可。
2.8 对比 JDK 7 的 ConcurrentHashMap 有什么区别?
- JDK8 中新增了红黑树;
- JDK7中使用的是头插法,JDK8中使用的是尾插法;
- JDK7中使用了分段锁,而JDK8中没有使用分段锁了;
- JDK7中使用了
ReentrantLock,JDK8中没有使用ReentrantLock了,而使用了Synchronized; - JDK7中的扩容是每个
Segment内部进行扩容,不会影响其他Segment,而JDK8中的扩容和HashMap的扩容类似,只不过支持了多线程扩容,并且保证了线程安全。 - 补充说明:JDK6 / 7中的
ConcurrentHashMap主要使用Segment来实现减小锁粒度,把HashMap分割成若干个Segment,在put的时候需要锁住Segment,get时候不加锁,使用volatile来保证可见性,当要统计全局时(比如size),首先会尝试多次计算 modcount 来确定,这几次尝试中,是否有其他线程进行了修改操作,如果没有,则直接返回size。如果有,则需要依次锁住所有的Segment来计算。JDK7中ConcurrentHashmap中,当长度过长碰撞会很频繁,链表的增改删查操作都会消耗很长的时间,影响性能。所以 JDK8 中完全重写了ConcurrentHashMap,代码量从原来的1000多行变成了 6000多行,实现上也和原来的分段式存储有很大的区别。
三、LinkedBlockingQueue
3.1 入队出队
- 入队源码:
public class LinkedBlockingQueue extends AbstractQueueimplements BlockingQueue, java.io.Serializable {static class Node {E item;/*** One of:* - the real successor Node* - this Node, meaning the successor is head.next* - null, meaning there is no successor (this is the last node)*/Node next;Node(E x) { item = x; }}
}
- 初始化链表:
last = head = new NodeDummy 节点用来占位,item 为 null。(null);

- 当一个节点入队
last = last.next = node;

- 再来一个节点入队
last = last.next = node;

- 出队源码:
/*** Removes a node from head of queue.** @return the node*/private E dequeue() {// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert head.item == null;Node h = head;Node first = h.next;h.next = h; // help GChead = first;E x = first.item;first.item = null;return x;}
- 示意图:

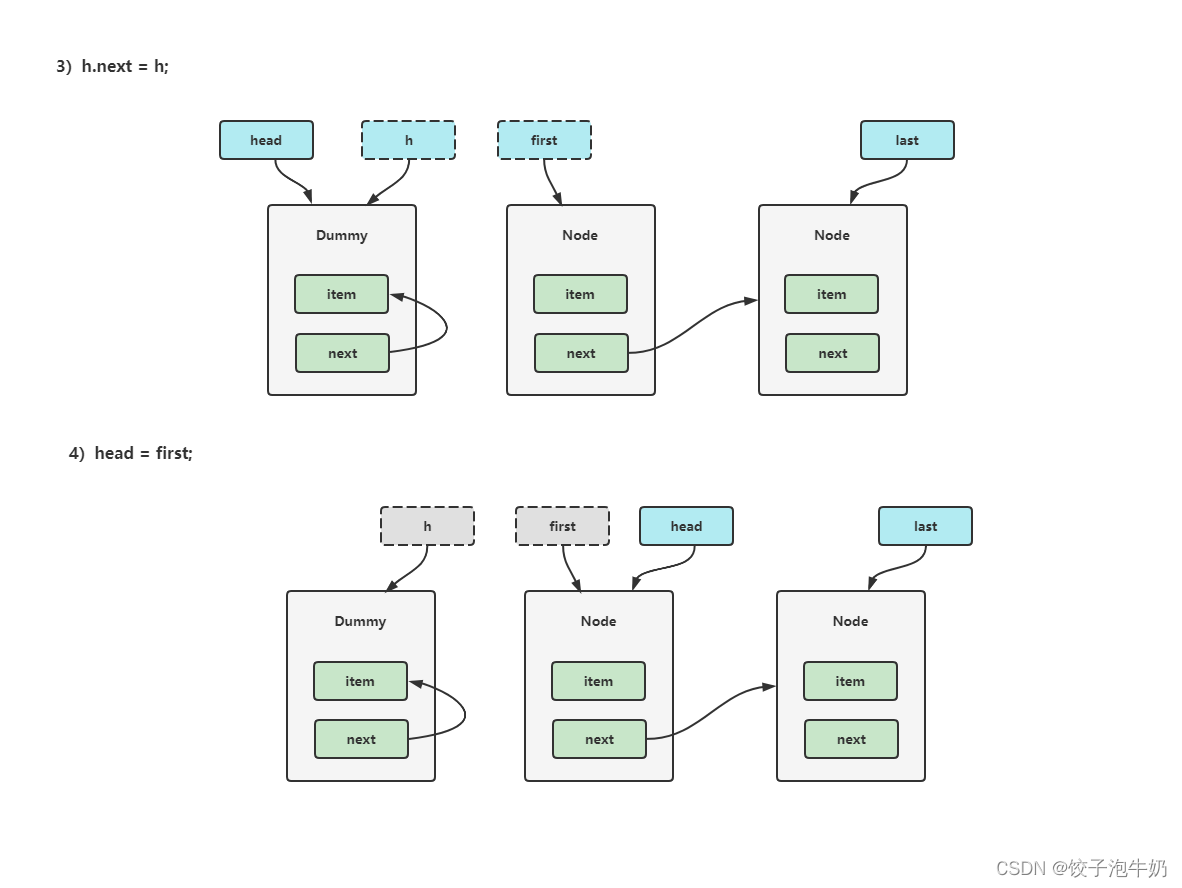
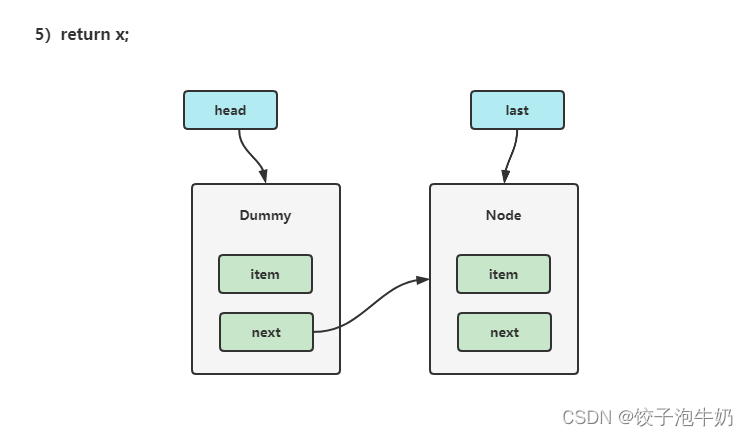
3.2 加锁分析
巧妙之处在于用了两把锁和
dummy(哑元)节点。
-
用一把锁,同一时刻,最多只允许有一个线程(生产者或消费者,二选一)执行。
-
用两把锁,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行:
-
消费者与消费者线程仍然串行。
-
生产者与生产者线程仍然串行。
-
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
3.3 线程安全分析
-
当节点总数大于 2 时(包括
dummy节点),putLock 保证的是last节点的线程安全,takeLock 保证的是head节点的线程安全。两把锁保证了入队和出队没有竞争。 -
当节点总数等于 2 时(即一个
dummy节点,一个正常节点)这时候,仍然是两把锁锁两个对象,不会竞争。 -
当节点总数等于 1 时(就一个
dummy节点)这时 take 线程会被 notEmpty 条件阻塞,有竞争,会阻塞。
3.4 源码分析
put():
/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if* necessary for space to become available.** @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}*/public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.int c = -1;Node node = new Node(e);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;// count 用来维护元素计数。final AtomicInteger count = this.count;putLock.lockInterruptibly();try {/** Note that count is used in wait guard even though it is* not protected by lock. This works because count can* only decrease at this point (all other puts are shut* out by lock), and we (or some other waiting put) are* signalled if it ever changes from capacity. Similarly* for all other uses of count in other wait guards.*/// 满了就等待。while (count.get() == capacity) {notFull.await();}// 有空位, 入队且计数加一。enqueue(node);c = count.getAndIncrement();// 除了自己 put 以外, 队列还有空位, 由自己叫醒其他 put 线程。if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}// 如果队列中有一个元素, 叫醒 take 线程。if (c == 0)// 这里调用的是 notEmpty.signal() 而不是 notEmpty.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争。signalNotEmpty();}
take():
public E take() throws InterruptedException {E x;int c = -1;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == 0) {notEmpty.await();}x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}// 如果队列中只有一个空位时, 叫醒 put 线程。// 如果有多个线程进行出队, 第一个线程满足 c == capacity, 但后续线程 c < capacity。if (c == capacity)// 这里调用的是 notFull.signal() 而不是 notFull.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争。signalNotFull();return x;}
3.5 性能比较
主要列举 LinkedBlockingQueue 与 ArrayBlockingQueue 的性能比较:
-
Linked 支持有界,Array 强制有界。
-
Linked 实现是链表,Array 实现是数组。
-
Linked 是懒惰的,而 Array 需要提前初始化 Node 数组。
-
Linked 每次入队会生成新 Node,而 Array 的 Node 是提前创建好的。
-
Linked 两把锁,Array 一把锁。
四、ConcurrentLinkedQueue
4.1 概述
ConcurrentLinkedQueue的设计与LinkedBlockingQueue非常像。
-
也是两把锁,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行;
-
dummy节点的引入让两把锁将来锁住的是不同对象,避免竞争; -
只是这锁使用了
cas来实现。
4.2 简单实现
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueTests {public static void main(String[] args) {MyQueue queue = new MyQueue<>();queue.offer("3");queue.offer("2");queue.offer("1");System.out.println(queue);// 3->2->1->null}
}class MyQueue implements Queue {private volatile Node head;private volatile Node last;public MyQueue() {head = last = new Node<>(null, null);}private static class Node {volatile E item;public Node(E item, Node next) {this.item = item;this.next = new AtomicReference<>(next);}AtomicReference> next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (Node p = head; p != null; p = p.next.get()) {E item = p.item;if (item != null) {sb.append(item).append("->");}}sb.append("null");return sb.toString();}@Overridepublic boolean offer(E e) {Node n = new Node<>(e, null);while (true) {// 获取尾节点AtomicReference> next = last.next;// S1: 真正尾节点的 next 是 null, cas 从 null 到新节点if (next.compareAndSet(null, n)) {// 这时的 last 已经是倒数第二, next 不为空了, 其它线程的 cas 肯定失败// S2: 更新 last 为倒数第一的节点last = n;return true;}}}@Overridepublic int size() {return 0;}@Overridepublic boolean isEmpty() {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean contains(Object o) {return false;}@Overridepublic Iterator iterator() {return null;}@Overridepublic Object[] toArray() {return new Object[0];}@Overridepublic T[] toArray(T[] a) {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean add(E e) {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object o) {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean containsAll(Collection c) {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean addAll(Collection c) {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean removeAll(Collection c) {return false;}@Overridepublic boolean retainAll(Collection c) {return false;}@Overridepublic void clear() {}@Overridepublic E remove() {return null;}@Overridepublic E poll() {return null;}@Overridepublic E element() {return null;}@Overridepublic E peek() {return null;}
}
五、CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArraySet是它的马甲 底层实现采用了 写入时拷贝 的思想,增删改操作会将底层数组拷贝一份,更改操作在新数组上执行,这时不影响其它线程的并发读,读写分离。
5.1 源码分析
- 此处以新增为例:
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list.** @param e element to be appended to this list* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/public boolean add(E e) {// 可重入锁。final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {// 获取旧的数组。Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;// 拷贝新的数组(这里是比较耗时的操作,但不影响其它读线程)。Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);// 添加新元素。newElements[len] = e;// 替换旧的数组。setArray(newElements);return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}
- 其他读操作并未加锁(适合读多写少场景),此处以遍历读取为例:
public void forEach(Consumer action) {if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) elements[i];action.accept(e);}}
5.2 弱一致性
get()及 迭代器都有弱一致性的特点。- 此处以迭代器为例:
public class CopyOnWriteArrayListTests {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {CopyOnWriteArrayList list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);Iterator iter = list.iterator();new Thread(() -> {list.remove(0);list.forEach(System.out::print);// 2 3System.out.println();}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);while (iter.hasNext()) {System.out.print(iter.next());// 1 2 3}}
}
- 注意(并不是弱一致性就不好):
- 数据库的
MVCC都是弱一致性的表现。 - 并发高和一致性是矛盾的,需要权衡。
- 数据库的
六、结束语
“-------怕什么真理无穷,进一寸有一寸的欢喜。”
微信公众号搜索:饺子泡牛奶。
上一篇:玩转MySQL:多姿多彩的SQL
